Hippocampus Abdominalis 1921 Waite Fishes S Austr FMIB 45602 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , ' seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the
 The earliest description of the ridge running along the floor of the temporal horn of the lateral ventricle comes from the Venetian anatomist Julius Caesar Aranzi (1587), who likened it first to a
The earliest description of the ridge running along the floor of the temporal horn of the lateral ventricle comes from the Venetian anatomist Julius Caesar Aranzi (1587), who likened it first to a
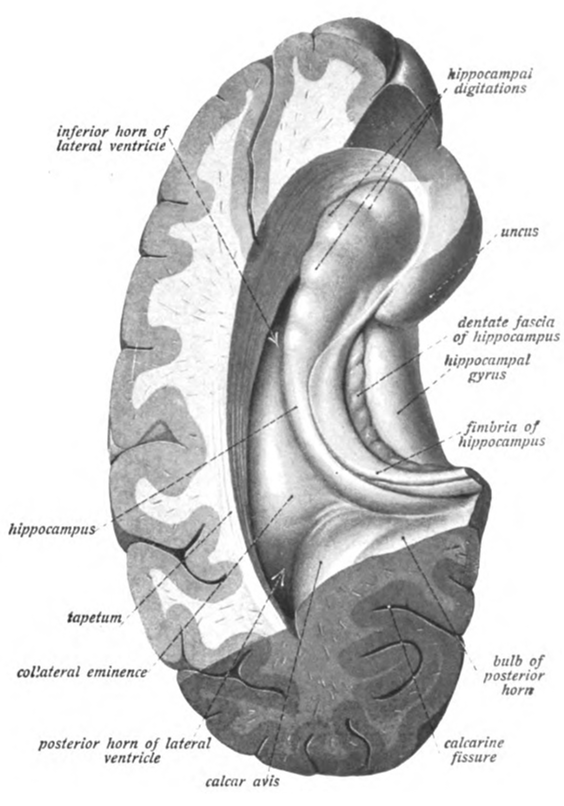
 The hippocampus can be seen as a ridge of gray matter tissue, elevating from the floor of each lateral ventricle in the region of the inferior or temporal horn. This ridge can also be seen as an inward fold of the archicortex into the medial temporal lobe. The hippocampus can only be seen in
The hippocampus can be seen as a ridge of gray matter tissue, elevating from the floor of each lateral ventricle in the region of the inferior or temporal horn. This ridge can also be seen as an inward fold of the archicortex into the medial temporal lobe. The hippocampus can only be seen in
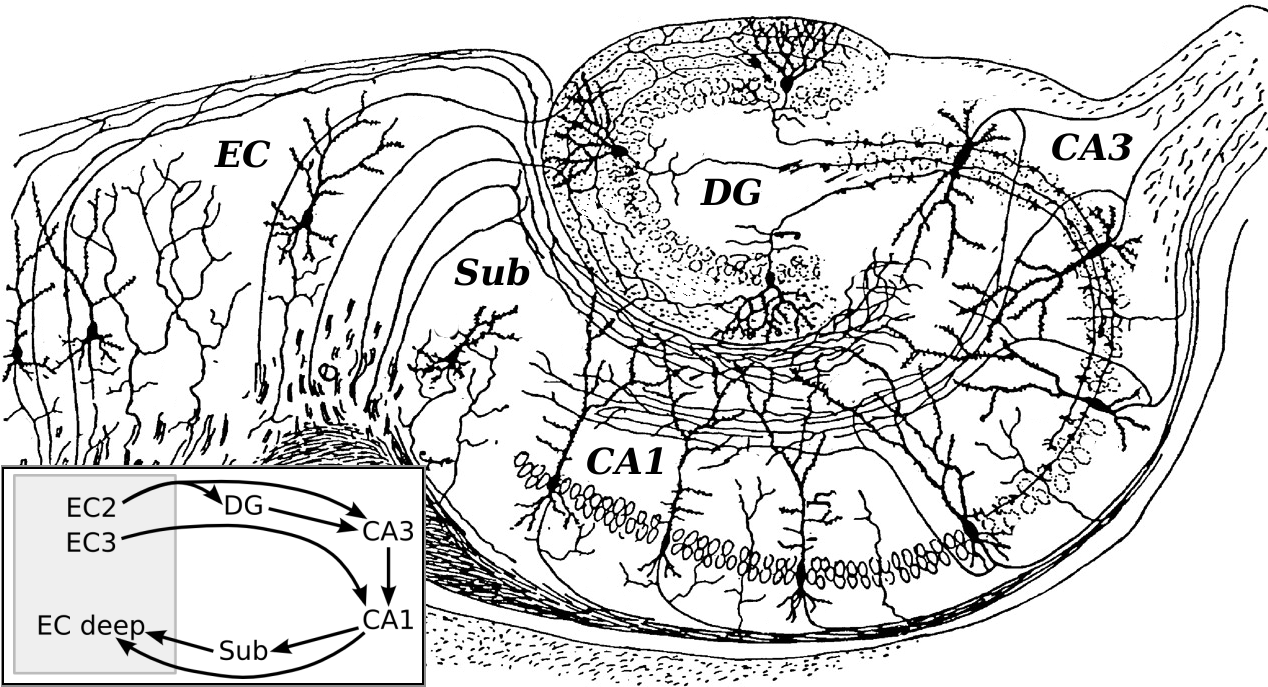 The major input to the hippocampus is through the entorhinal cortex (EC), whereas its major output is via CA1 to the subiculum. Kandel, 2012 Information reaches CA1 via two main pathways, direct and indirect. Axons from the EC that originate in layer III are the origin of the direct perforant pathway and form synapses on the very distal apical dendrites of CA1 neurons. Conversely, axons originating from layer II are the origin of the indirect pathway, and information reaches CA1 via the
The major input to the hippocampus is through the entorhinal cortex (EC), whereas its major output is via CA1 to the subiculum. Kandel, 2012 Information reaches CA1 via two main pathways, direct and indirect. Axons from the EC that originate in layer III are the origin of the direct perforant pathway and form synapses on the very distal apical dendrites of CA1 neurons. Conversely, axons originating from layer II are the origin of the indirect pathway, and information reaches CA1 via the
 Areas of the hippocampus are shown to be functionally and anatomically distinct. The dorsal hippocampus (DH), ventral hippocampus (VH) and intermediate hippocampus serve different functions, project with differing pathways, and have varying degrees of place cells. Fanselow, 2010 The dorsal hippocampus serves for spatial memory, verbal memory, and learning of conceptual information. Using the radial arm maze, lesions in the DH were shown to cause spatial memory impairment while VH lesions did not. Its projecting pathways include the medial septal nucleus and
Areas of the hippocampus are shown to be functionally and anatomically distinct. The dorsal hippocampus (DH), ventral hippocampus (VH) and intermediate hippocampus serve different functions, project with differing pathways, and have varying degrees of place cells. Fanselow, 2010 The dorsal hippocampus serves for spatial memory, verbal memory, and learning of conceptual information. Using the radial arm maze, lesions in the DH were shown to cause spatial memory impairment while VH lesions did not. Its projecting pathways include the medial septal nucleus and
 The third important theory of hippocampal function relates the hippocampus to space. The spatial theory was originally championed by O'Keefe and Nadel, who were influenced by American psychologist E.C. Tolman's theories about " cognitive maps" in humans and animals. O'Keefe and his student Dostrovsky in 1971 discovered neurons in the rat hippocampus that appeared to them to show activity related to the rat's location within its environment. Despite skepticism from other investigators, O'Keefe and his co-workers, especially Lynn Nadel, continued to investigate this question, in a line of work that eventually led to their very influential 1978 book ''The Hippocampus as a Cognitive Map''. O'Keefe and Nadel, 1978 There is now almost universal agreement that hippocampal function plays an important role in spatial coding, but the details are widely debated. Moser et al., 2008
Later research has focused on trying to bridge the disconnect between the two main views of hippocampal function as being split between memory and spatial cognition. In some studies, these areas have been expanded to the point of near convergence. In an attempt to reconcile the two disparate views, it is suggested that a broader view of the hippocampal function is taken and seen to have a role that encompasses both the organisation of experience ( mental mapping, as per Tolman's original concept in 1948) and the directional behaviour seen as being involved in all areas of cognition, so that the function of the hippocampus can be viewed as a broader system that incorporates both the memory and the spatial perspectives in its role that involves the use of a wide scope of cognitive maps. This relates to the
The third important theory of hippocampal function relates the hippocampus to space. The spatial theory was originally championed by O'Keefe and Nadel, who were influenced by American psychologist E.C. Tolman's theories about " cognitive maps" in humans and animals. O'Keefe and his student Dostrovsky in 1971 discovered neurons in the rat hippocampus that appeared to them to show activity related to the rat's location within its environment. Despite skepticism from other investigators, O'Keefe and his co-workers, especially Lynn Nadel, continued to investigate this question, in a line of work that eventually led to their very influential 1978 book ''The Hippocampus as a Cognitive Map''. O'Keefe and Nadel, 1978 There is now almost universal agreement that hippocampal function plays an important role in spatial coding, but the details are widely debated. Moser et al., 2008
Later research has focused on trying to bridge the disconnect between the two main views of hippocampal function as being split between memory and spatial cognition. In some studies, these areas have been expanded to the point of near convergence. In an attempt to reconcile the two disparate views, it is suggested that a broader view of the hippocampal function is taken and seen to have a role that encompasses both the organisation of experience ( mental mapping, as per Tolman's original concept in 1948) and the directional behaviour seen as being involved in all areas of cognition, so that the function of the hippocampus can be viewed as a broader system that incorporates both the memory and the spatial perspectives in its role that involves the use of a wide scope of cognitive maps. This relates to the
 Studies on freely moving rats and mice have shown many hippocampal neurons to act as
Studies on freely moving rats and mice have shown many hippocampal neurons to act as
 The hippocampus shows two major "modes" of activity, each associated with a distinct pattern of
The hippocampus shows two major "modes" of activity, each associated with a distinct pattern of
 The underlying currents producing the theta wave are generated mainly by densely packed neural layers of the entorhinal cortex, CA3, and the dendrites of pyramidal cells. The theta wave is one of the largest signals seen on EEG, and is known as the hippocampal theta rhythm. Buzsáki, 2002 In some situations the EEG is dominated by regular waves at 3 to 10 Hz, often continuing for many seconds. These reflect subthreshold
The underlying currents producing the theta wave are generated mainly by densely packed neural layers of the entorhinal cortex, CA3, and the dendrites of pyramidal cells. The theta wave is one of the largest signals seen on EEG, and is known as the hippocampal theta rhythm. Buzsáki, 2002 In some situations the EEG is dominated by regular waves at 3 to 10 Hz, often continuing for many seconds. These reflect subthreshold

 The hippocampus is one of the few brain regions where new neurons are generated. This process of
The hippocampus is one of the few brain regions where new neurons are generated. This process of

File:Hippocampus coronal sections.gif, Hippocampus highlighted in green on coronal T1 MRI images
File:Hippocampus sagittal sections.gif, Hippocampus highlighted in green on sagittal T1 MRI images
File:Hippocampus transversal sections.gif, Hippocampus highlighted in green on transversal T1 MRI images
''Hippocampus''
(Wiley) * *
Hippocampus – Cell Centered Database
Temporal-lobe.com An interactive diagram of the rat parahippocampal-hippocampal region
Search Hippocampus on BrainNavigator
via BrainNavigator {{Authority control Limbic system
limbic system
The limbic system, also known as the paleomammalian cortex, is a set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, immediately beneath the medial temporal lobe of the cerebrum primarily in the forebrain.Schacter, Daniel L. 2012. ''Ps ...
, and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory
Short-term memory (or "primary" or "active memory") is the capacity for holding a small amount of information in an active, readily available state for a short interval. For example, short-term memory holds a phone number that has just been recit ...
to long-term memory, and in spatial memory
In cognitive psychology and neuroscience, spatial memory is a form of memory responsible for the recording and recovery of information needed to plan a course to a location and to recall the location of an object or the occurrence of an event. Sp ...
that enables navigation. The hippocampus is located in the allocortex, with neural projections into the neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, sp ...
in humans, as well as primates. The hippocampus, as the medial pallium, is a structure found in all vertebrates. In humans, it contains two main interlocking parts: the hippocampus proper (also called ''Ammon's horn''), and the dentate gyrus.
In Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term me ...
(and other forms of dementia), the hippocampus is one of the first regions of the brain to suffer damage; short-term memory loss and disorientation
Orientation is a function of the mind involving awareness of three dimensions: time, Location (geography), place and person. Problems with orientation lead to ''dis''orientation, and can be due to various conditions, from delirium to Substance int ...
are included among the early symptoms. Damage to the hippocampus can also result from oxygen starvation (hypoxia
Hypoxia means a lower than normal level of oxygen, and may refer to:
Reduced or insufficient oxygen
* Hypoxia (environmental), abnormally low oxygen content of the specific environment
* Hypoxia (medical), abnormally low level of oxygen in the tis ...
), encephalitis
Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain. The severity can be variable with symptoms including reduction or alteration in consciousness, headache, fever, confusion, a stiff neck, and vomiting. Complications may include seizures, hallucinations, ...
, or medial temporal lobe epilepsy. People with extensive, bilateral hippocampal damage may experience anterograde amnesia: the inability to form and retain new memories.
Since different neuronal cell types are neatly organized into layers in the hippocampus, it has frequently been used as a model system for studying neurophysiology. The form of neural plasticity known as long-term potentiation (LTP) was initially discovered to occur in the hippocampus and has often been studied in this structure. LTP is widely believed to be one of the main neural mechanisms by which memories are stored in the brain.
In rodents as model organism
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workin ...
s, the hippocampus has been studied extensively as part of a brain system responsible for spatial memory
In cognitive psychology and neuroscience, spatial memory is a form of memory responsible for the recording and recovery of information needed to plan a course to a location and to recall the location of an object or the occurrence of an event. Sp ...
and navigation. Many neurons in the rat
Rats are various medium-sized, long-tailed rodents. Species of rats are found throughout the order Rodentia, but stereotypical rats are found in the genus ''Rattus''. Other rat genera include ''Neotoma'' ( pack rats), ''Bandicota'' (bandicoot ...
and mouse
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
hippocampus respond as place cell
A place cell is a kind of pyramidal neuron in the hippocampus that becomes active when an animal enters a particular place in its environment, which is known as the place field. Place cells are thought to act collectively as a cognitive repres ...
s: that is, they fire bursts of action potentials when the animal passes through a specific part of its environment. Hippocampal place cells interact extensively with head direction cells, whose activity acts as an inertial compass, and conjecturally with grid cells in the neighboring entorhinal cortex.
Name
silkworm
The domestic silk moth (''Bombyx mori''), is an insect from the moth family Bombycidae. It is the closest relative of ''Bombyx mandarina'', the wild silk moth. The silkworm is the larva or caterpillar of a silk moth. It is an economically imp ...
and then to a seahorse ( Latin ''hippocampus'', from Greek ἱππόκαμπος, from ἵππος, 'horse' + κάμπος, 'sea monster'). The German anatomist Duvernoy (1729), the first to illustrate the structure, also wavered between "seahorse" and "silkworm". "Ram's horn" was proposed by the Danish anatomist Jacob Winsløw
Jacob Benignus Winsløw, also known as Jacques-Bénigne Winslow (17 April 1669 – 3 April 1760), was a Danish-born French anatomist.
Life
Winsløw was born in Odense, Denmark. Later he became a pupil and successor of Guichard Joseph Duverney, ...
in 1732; and a decade later his fellow Parisian, the surgeon de Garengeot, used ''cornu Ammonis'' – horn of Amun
Amun (; also ''Amon'', ''Ammon'', ''Amen''; egy, jmn, reconstructed as (Old Egyptian and early Middle Egyptian) → (later Middle Egyptian) → (Late Egyptian), cop, Ⲁⲙⲟⲩⲛ, Amoun) romanized: ʾmn) was a major ancient Egyptian ...
, Duvernoy, 2005 the ancient Egyptian god who was often represented as having a ram's head.
Another reference appeared with the term ''pes hippocampi
The lower end of the hippocampus
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , 'seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampu ...
'', which may date back to Diemerbroeck in 1672, introducing a comparison with the shape of the folded back forelimbs and webbed feet of the mythological hippocampus, a sea monster with a horse's forequarters and a fish's tail. The hippocampus was then described as ''pes hippocampi major'', with an adjacent bulge in the occipital horn, described as the ''pes hippocampi minor'' and later renamed as the calcar avis. The renaming of the hippocampus as hippocampus major, and the calcar avis as hippocampus minor, has been attributed to Félix Vicq-d'Azyr systematizing nomenclature of parts of the brain in 1786. Mayer Mayer may refer to:
*Mayer (name)
Places
* C. Mayer (crater), named after Christian Mayer
* Mayer, Syria
* Mayer, Arizona, United States
* Mayer, Minnesota, United States
* Mayersville, Mississippi, United States
* Mayerthorpe, Alberta, Canad ...
mistakenly used the term hippopotamus in 1779, and was followed by some other authors until Karl Friedrich Burdach
Karl Friedrich Burdach (12 June 1776 – 16 July 1847) was a German physiologist. He was born in Leipzig and died in Königsberg. He was the first to use the word "biology" and was a pioneer of neuroanatomy.
Life
Burdach came from a family of ...
resolved this error in 1829. In 1861 the hippocampus minor became the center of a dispute over human evolution between Thomas Henry Huxley and Richard Owen
Sir Richard Owen (20 July 1804 – 18 December 1892) was an English biologist, comparative anatomist and paleontologist. Owen is generally considered to have been an outstanding naturalist with a remarkable gift for interpreting fossils.
Owe ...
, satirized as the Great Hippocampus Question. The term hippocampus minor fell from use in anatomy textbooks and was officially removed in the Nomina Anatomica
''Nomina Anatomica'' (''NA'') was the international standard on human anatomic terminology from 1895 until it was replaced by ''Terminologia Anatomica'' in 1998.
In the late nineteenth century some 30,000 terms for various body parts were in use ...
of 1895. Today, the structure is just called the hippocampus, with the term ''cornu Ammonis'' (that is, 'Ammon's horn') surviving in the names of the hippocampal subfields CA1-CA4.
Relation to limbic system
The term ''limbic system'' was introduced in 1952 by Paul MacLean to describe the set of structures that line the deep edge of the cortex (Latin ''limbus'' meaning ''border''): These include the hippocampus,cingulate cortex
The cingulate cortex is a part of the brain situated in the medial aspect of the cerebral cortex. The cingulate cortex includes the entire cingulate gyrus, which lies immediately above the corpus callosum, and the continuation of this in the ci ...
, olfactory cortex
The olfactory system, or sense of smell, is the sensory system used for smelling (olfaction). Olfaction is one of the special senses, that have directly associated specific organs. Most mammals and reptiles have a main olfactory system and an ac ...
, and amygdala. Paul MacLean later suggested that the limbic structures comprise the neural basis of emotion. The hippocampus is anatomically connected to parts of the brain that are involved with emotional behaviorthe septum
In biology, a septum (Latin for ''something that encloses''; plural septa) is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones. A cavity or structure divided in this way may be referred to as septate.
Examples
Human anatomy
* Interatri ...
, the hypothalamic
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus i ...
mammillary body, and the anterior nuclear complex in the thalamus, and is generally accepted to be part of the limbic system.
Anatomy

 The hippocampus can be seen as a ridge of gray matter tissue, elevating from the floor of each lateral ventricle in the region of the inferior or temporal horn. This ridge can also be seen as an inward fold of the archicortex into the medial temporal lobe. The hippocampus can only be seen in
The hippocampus can be seen as a ridge of gray matter tissue, elevating from the floor of each lateral ventricle in the region of the inferior or temporal horn. This ridge can also be seen as an inward fold of the archicortex into the medial temporal lobe. The hippocampus can only be seen in dissection
Dissection (from Latin ' "to cut to pieces"; also called anatomization) is the dismembering of the body of a deceased animal or plant to study its anatomical structure. Autopsy is used in pathology and forensic medicine to determine the cause o ...
s as it is concealed by the parahippocampal gyrus. Amaral and Lavenex, 2006 The cortex thins from six layers to the three or four layers that make up the hippocampus.
The term hippocampal formation is used to refer to the hippocampus proper and its related parts. However, there is no consensus as to what parts are included. Sometimes the hippocampus is said to include the dentate gyrus and the subiculum. Some references include the dentate gyrus and the subiculum in the hippocampal formation, and others also include the presubiculum, parasubiculum
In the rodent, the parasubiculum is a retrohippocampal isocortical structure, and a major component of the subicular complex. It receives numerous subcortical and cortical inputs, and sends major projections to the superficial layers of the entor ...
, and entorhinal cortex. The neural layout and pathways within the hippocampal formation are very similar in all mammals.
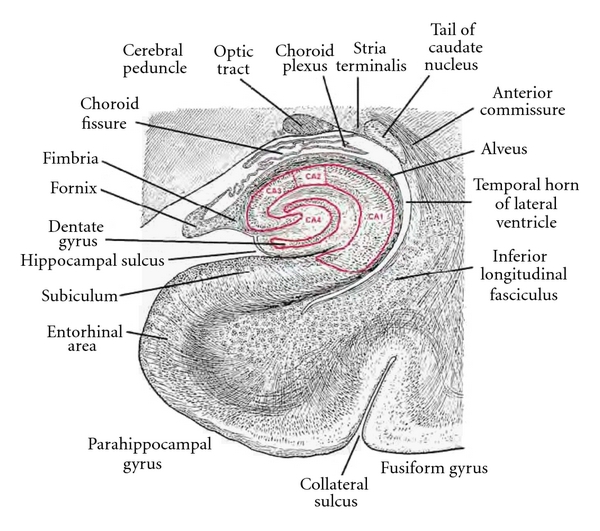
The hippocampus, including the dentate gyrus, has the shape of a curved tube, which has been compared to a seahorse, and to a horn of a ram, which after the ancient Egyptian god often portrayed as such takes the name ''cornu Ammonis''. Its abbreviation CA is used in naming the hippocampal subfields CA1, CA2, CA3, and CA4. It can be distinguished as an area where the cortex narrows into a single layer of densely packed pyramidal neurons, which curl into a tight U shape. One edge of the "U," – CA4, is embedded into the backward-facing, flexed dentate gyrus. The hippocampus is described as having an anterior and posterior part (in primates) or a ventral and dorsal part in other animals. Both parts are of similar composition but belong to different neural circuit
A neural circuit is a population of neurons interconnected by synapses to carry out a specific function when activated. Neural circuits interconnect to one another to form large scale brain networks.
Biological neural networks have inspired the ...
s. In the rat, the two hippocampi resemble a pair of bananas, joined at the stems by the commissure of fornix (also called the hippocampal commissure). In primates, the part of the hippocampus at the bottom, near the base of the temporal lobe, is much broader than the part at the top. This means that in cross-section the hippocampus can show a number of different shapes, depending on the angle and location of the cut.
In a cross-section of the hippocampus, including the dentate gyrus, several layers will be shown. The dentate gyrus has three layers of cells (or four if the hilus is included). The layers are from the outer in – the ''molecular layer'', the ''inner molecular layer'', the ''granular layer'', and the ''hilus''. The CA3 in the hippocampus proper has the following cell layers known as strata: lacunosum-moleculare, radiatum, lucidum, pyramidal, and oriens. CA2 and CA1 also have these layers except the lucidum stratum.
The input to the hippocampus (from varying cortical and subcortical structures) comes from the entorhinal cortex via the perforant path. The entorhinal cortex (EC) is strongly and reciprocally connected with many cortical and subcortical structures as well as with the brainstem. Different thalamic nuclei, (from the anterior and midline groups), the medial septal nucleus
The medial septal nucleus (MS) is one of the septal nuclei. Neurons in this nucleus give rise to the bulk of efferents from the septal nuclei. A major projection from the medial septal nucleus terminates in the hippocampal formation.
It plays a ro ...
, the supramammillary nucleus The supramammillary nucleus (SuM), or supramammillary area, is a thin layer of cells in the brain that lies above the mammillary bodies. It can be considered part of the hypothalamus and diencephalon. The nucleus can be divided into medial and later ...
of the hypothalamus, and the raphe nuclei and locus coeruleus
The locus coeruleus () (LC), also spelled locus caeruleus or locus ceruleus, is a nucleus in the pons of the brainstem involved with physiological responses to stress and panic. It is a part of the reticular activating system.
The locus coerule ...
of the brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is cont ...
all send axons to the EC, so that it serves as the interface between the neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, sp ...
and the other connections, and the hippocampus.
The EC is located in the parahippocampal gyrus, a cortical region adjacent to the hippocampus. This gyrus conceals the hippocampus. The parahippocampal gyrus is adjacent to the perirhinal cortex, which plays an important role in the visual recognition of complex objects. There is also substantial evidence that it makes a contribution to memory, which can be distinguished from the contribution of the hippocampus. It is apparent that complete amnesia
Amnesia is a deficit in memory caused by brain damage or disease,Gazzaniga, M., Ivry, R., & Mangun, G. (2009) Cognitive Neuroscience: The biology of the mind. New York: W.W. Norton & Company. but it can also be caused temporarily by the use ...
occurs only when both the hippocampus and the parahippocampus are damaged. Eichenbaum et al., 2007
Circuitry
 The major input to the hippocampus is through the entorhinal cortex (EC), whereas its major output is via CA1 to the subiculum. Kandel, 2012 Information reaches CA1 via two main pathways, direct and indirect. Axons from the EC that originate in layer III are the origin of the direct perforant pathway and form synapses on the very distal apical dendrites of CA1 neurons. Conversely, axons originating from layer II are the origin of the indirect pathway, and information reaches CA1 via the
The major input to the hippocampus is through the entorhinal cortex (EC), whereas its major output is via CA1 to the subiculum. Kandel, 2012 Information reaches CA1 via two main pathways, direct and indirect. Axons from the EC that originate in layer III are the origin of the direct perforant pathway and form synapses on the very distal apical dendrites of CA1 neurons. Conversely, axons originating from layer II are the origin of the indirect pathway, and information reaches CA1 via the trisynaptic circuit The trisynaptic circuit, or trisynaptic loop is a relay of Neurotransmission, synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. The circuit was initially described by the neuroanatomist Santiago Ramón y Cajal, Santiago Ramon y Cajal, in the early twentiet ...
. In the initial part of this pathway, the axons project through the perforant pathway to the granule cells of the dentate gyrus (first synapse). From then, the information follows via the mossy fibres to CA3 (second synapse). From there, CA3 axons called Schaffer collaterals Schaffer collaterals are axon collaterals given off by CA3 pyramidal cells in the hippocampus. These collaterals project to area CA1 of the hippocampus and are an integral part of memory formation and the emotional network of the Papez circuit, an ...
leave the deep part of the cell body
The soma (pl. ''somata'' or ''somas''), perikaryon (pl. ''perikarya''), neurocyton, or cell body is the bulbous, non-process portion of a neuron or other brain cell type, containing the cell nucleus. The word 'soma' comes from the Greek '' σῶμ ...
and loop up to the apical dendrites and then extend to CA1 (third synapse). Axons from CA1 then project back to the entorhinal cortex, completing the circuit.
Basket cells in CA3 receive excitatory input from the pyramidal cells and then give an inhibitory feedback to the pyramidal cells. This ''recurrent inhibition'' is a simple feedback circuit that can dampen excitatory responses in the hippocampus. The pyramidal cells gives a ''recurrent excitation'' which is an important mechanism found in some memory processing microcircuits.
Several other connections play important roles in hippocampal function. Beyond the output to the EC, additional output pathways go to other cortical areas including the prefrontal cortex. A major output goes via the fornix to the lateral septal area and to the mammillary body of the hypothalamus (which the fornix interconnects with the hippocampus). The hippocampus receives modulatory input from the serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vas ...
, norepinephrine, and dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic compound, organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine const ...
systems, and from the nucleus reuniens
The nucleus reuniens is a region of the thalamic midline nuclear group. In the human brain, it is located in the interthalamic adhesion (''massa intermedia'').
The nucleus reuniens receives afferent input from a large number of structures, main ...
of the thalamus to field CA1. A very important projection comes from the medial septal nucleus, which sends cholinergic, and gamma amino butyric acid
Gamma (uppercase , lowercase ; ''gámma'') is the third letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 3. In Ancient Greek, the letter gamma represented a voiced velar stop . In Modern Greek, this letter re ...
(GABA) stimulating fibers (GABAergic fibers) to all parts of the hippocampus. The inputs from the medial septal nucleus play a key role in controlling the physiological state of the hippocampus; destruction of this nucleus abolishes the hippocampal theta rhythm
Theta waves generate the theta rhythm, a neural oscillation in the brain that underlies various aspects of cognition and behavior, including learning, memory, and spatial navigation in many animals. It can be recorded using various electrophysi ...
and severely impairs certain types of memory.
Regions
 Areas of the hippocampus are shown to be functionally and anatomically distinct. The dorsal hippocampus (DH), ventral hippocampus (VH) and intermediate hippocampus serve different functions, project with differing pathways, and have varying degrees of place cells. Fanselow, 2010 The dorsal hippocampus serves for spatial memory, verbal memory, and learning of conceptual information. Using the radial arm maze, lesions in the DH were shown to cause spatial memory impairment while VH lesions did not. Its projecting pathways include the medial septal nucleus and
Areas of the hippocampus are shown to be functionally and anatomically distinct. The dorsal hippocampus (DH), ventral hippocampus (VH) and intermediate hippocampus serve different functions, project with differing pathways, and have varying degrees of place cells. Fanselow, 2010 The dorsal hippocampus serves for spatial memory, verbal memory, and learning of conceptual information. Using the radial arm maze, lesions in the DH were shown to cause spatial memory impairment while VH lesions did not. Its projecting pathways include the medial septal nucleus and supramammillary nucleus The supramammillary nucleus (SuM), or supramammillary area, is a thin layer of cells in the brain that lies above the mammillary bodies. It can be considered part of the hypothalamus and diencephalon. The nucleus can be divided into medial and later ...
. The dorsal hippocampus also has more place cells than both the ventral and intermediate hippocampal regions.
The intermediate hippocampus has overlapping characteristics with both the ventral and dorsal hippocampus. Using anterograde tracing In neuroscience, anterograde tracing is a research method which is used to trace axonal projections from their source (the cell body or soma) to their point of termination (the synapse). A hallmark of anterograde tracing is the labeling of the pres ...
methods, Cenquizca and Swanson (2007) located the moderate projections to two primary olfactory cortical areas and prelimbic areas of the medial prefrontal cortex. This region has the smallest number of place cells. The ventral hippocampus functions in fear conditioning and affective processes. Anagnostaras ''et al.'' (2002) showed that alterations to the ventral hippocampus reduced the amount of information sent to the amygdala by the dorsal and ventral hippocampus, consequently altering fear conditioning in rats. Historically, the earliest widely held hypothesis was that the hippocampus is involved in olfaction
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste.
In humans, it ...
. This idea was cast into doubt by a series of anatomical studies that did not find any direct projections to the hippocampus from the olfactory bulb. However, later work did confirm that the olfactory bulb does project into the ventral part of the lateral entorhinal cortex, and field CA1 in the ventral hippocampus sends axons to the main olfactory bulb, the anterior olfactory nucleus, and to the primary olfactory cortex. There continues to be some interest in hippocampal olfactory responses, in particular, the role of the hippocampus in memory for odors, but few specialists today believe that olfaction is its primary function.
Function
Theories of hippocampal functions
Over the years, three main ideas of hippocampal function have dominated the literature:response inhibition
Inhibitory control, also known as response inhibition, is a cognitive process – and, more specifically, an executive function – that permits an individual to inhibit their impulses and natural, habitual, or dominant behavioral res ...
, episodic memory, and spatial cognition. The behavioral inhibition theory (caricatured by John O'Keefe and Lynn Nadel as "slam on the brakes!") was very popular up to the 1960s. It derived much of its justification from two observations: first, that animals with hippocampal damage tend to be hyperactive; second, that animals with hippocampal damage often have difficulty learning to inhibit responses that they have previously been taught, especially if the response requires remaining quiet as in a passive avoidance test. British psychologist Jeffrey Gray developed this line of thought into a full-fledged theory of the role of the hippocampus in anxiety. The inhibition theory is currently the least popular of the three.
The second major line of thought relates the hippocampus to memory. Although it had historical precursors, this idea derived its main impetus from a famous report by American neurosurgeon William Beecher Scoville
William Beecher Scoville (January 13, 1906 – February 25, 1984) was an American neurosurgeon at Hartford Hospital in Hartford, Connecticut. Scoville established the Department of Neurosurgery at Connecticut's Hartford Hospital in 1939. He perfo ...
and British-Canadian neuropsychologist Brenda Milner Scoville and Milner, 1957 describing the results of surgical destruction of the hippocampi when trying to relieve epileptic seizures in an American man Henry Molaison
Henry Gustav Molaison (February 26, 1926 – December 2, 2008), known widely as H.M., was an American who had a bilateral medial temporal lobe, temporal lobectomy to surgically resect the anterior two thirds of his Hippocampus, hippocampi, p ...
, New York Times, 12-06-2008 known until his death in 2008 as "Patient H.M." The unexpected outcome of the surgery was severe anterograde and partial retrograde amnesia; Molaison was unable to form new episodic memories after his surgery and could not remember any events that occurred just before his surgery, but he did retain memories of events that occurred many years earlier extending back into his childhood. This case attracted such widespread professional interest that Molaison became the most intensively studied subject in medical history. In the ensuing years, other patients with similar levels of hippocampal damage and amnesia (caused by accident or disease) have also been studied, and thousands of experiments have studied the physiology of activity-driven changes in synaptic connections in the hippocampus. There is now universal agreement that the hippocampi play some sort of important role in memory; however, the precise nature of this role remains widely debated. Squire, 1992 Eichenbaum and Cohen, 1993 A recent theory proposed – without questioning its role in spatial cognition – that the hippocampus encodes new episodic memories by associating representations in the newborn granule cells
A granule is a large particle or grain. It can refer to:
* Granule (cell biology), any of several submicroscopic structures, some with explicable origins, others noted only as cell type-specific features of unknown function
** Azurophilic granul ...
of the dentate gyrus and arranging those representations sequentially in the CA3 by relying on the phase precession
Phase precession is a neurophysiological process in which the time of firing of action potentials by individual neurons occurs progressively earlier in relation to the phase of the local field potential oscillation with each successive cycle. In ...
generated in the entorhinal cortex
 The third important theory of hippocampal function relates the hippocampus to space. The spatial theory was originally championed by O'Keefe and Nadel, who were influenced by American psychologist E.C. Tolman's theories about " cognitive maps" in humans and animals. O'Keefe and his student Dostrovsky in 1971 discovered neurons in the rat hippocampus that appeared to them to show activity related to the rat's location within its environment. Despite skepticism from other investigators, O'Keefe and his co-workers, especially Lynn Nadel, continued to investigate this question, in a line of work that eventually led to their very influential 1978 book ''The Hippocampus as a Cognitive Map''. O'Keefe and Nadel, 1978 There is now almost universal agreement that hippocampal function plays an important role in spatial coding, but the details are widely debated. Moser et al., 2008
Later research has focused on trying to bridge the disconnect between the two main views of hippocampal function as being split between memory and spatial cognition. In some studies, these areas have been expanded to the point of near convergence. In an attempt to reconcile the two disparate views, it is suggested that a broader view of the hippocampal function is taken and seen to have a role that encompasses both the organisation of experience ( mental mapping, as per Tolman's original concept in 1948) and the directional behaviour seen as being involved in all areas of cognition, so that the function of the hippocampus can be viewed as a broader system that incorporates both the memory and the spatial perspectives in its role that involves the use of a wide scope of cognitive maps. This relates to the
The third important theory of hippocampal function relates the hippocampus to space. The spatial theory was originally championed by O'Keefe and Nadel, who were influenced by American psychologist E.C. Tolman's theories about " cognitive maps" in humans and animals. O'Keefe and his student Dostrovsky in 1971 discovered neurons in the rat hippocampus that appeared to them to show activity related to the rat's location within its environment. Despite skepticism from other investigators, O'Keefe and his co-workers, especially Lynn Nadel, continued to investigate this question, in a line of work that eventually led to their very influential 1978 book ''The Hippocampus as a Cognitive Map''. O'Keefe and Nadel, 1978 There is now almost universal agreement that hippocampal function plays an important role in spatial coding, but the details are widely debated. Moser et al., 2008
Later research has focused on trying to bridge the disconnect between the two main views of hippocampal function as being split between memory and spatial cognition. In some studies, these areas have been expanded to the point of near convergence. In an attempt to reconcile the two disparate views, it is suggested that a broader view of the hippocampal function is taken and seen to have a role that encompasses both the organisation of experience ( mental mapping, as per Tolman's original concept in 1948) and the directional behaviour seen as being involved in all areas of cognition, so that the function of the hippocampus can be viewed as a broader system that incorporates both the memory and the spatial perspectives in its role that involves the use of a wide scope of cognitive maps. This relates to the purposive behaviorism
Purposive behaviorism is a branch of psychology that was introduced by Edward Tolman. It combines the study of behavior while also considering the purpose or goal of behavior.Schultz, D.P. & Schultz, S.E. (2012). ''A history of modern psychology. ...
born of Tolman's original goal of identifying the complex cognitive mechanisms and purposes that guided behaviour.
It has also been proposed that the spiking activity of hippocampal neurons is associated spatially, and it was suggested that the mechanisms of memory and planning both evolved from mechanisms of navigation and that their neuronal algorithms were basically the same.
Many studies have made use of neuroimaging techniques such as functional magnetic resonance imaging
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area o ...
(fMRI), and a functional role in approach-avoidance conflict Approach-avoidance conflicts as elements of stress (biology), stress were first introduced by psychologist Kurt Lewin, one of the founders of modern social psychology.
Overview
Approach-avoidance conflicts occur when there is one goal or event that ...
has been noted. The anterior hippocampus is seen to be involved in decision-making under approach-avoidance conflict processing. It is suggested that the memory, spatial cognition, and conflict processing functions may be seen as working together and not mutually exclusive.
Role in memory
Psychologist
A psychologist is a professional who practices psychology and studies mental states, perceptual, cognitive, emotional, and social processes and behavior. Their work often involves the experimentation, observation, and interpretation of how indi ...
s and neuroscientists generally agree that the hippocampus plays an important role in the formation of new memories about experienced events (episodic
Episodic may refer to:
* The nature of television series that are divided into short programs known as episodes
* Episodic memory, types of memory that result from specific incidents in a lifetime
* In Geology, episodic refers to events that occur ...
or autobiographical memory). Squire and Schacter, 2002 Part of this function is hippocampal involvement in the detection of new events, places and stimuli. Some researchers regard the hippocampus as part of a larger medial temporal lobe memory system responsible for general declarative memory (memories that can be explicitly verbalizedthese would include, for example, memory for facts in addition to episodic memory). The hippocampus also encodes emotional context from the amygdala. This is partly why returning to a location where an emotional event occurred may evoke that emotion. There is a deep emotional connection between episodic memories and places.
Due to bilateral symmetry
Symmetry in biology refers to the symmetry observed in organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria. External symmetry can be easily seen by just looking at an organism. For example, take the face of a human being which has a pla ...
the brain has a hippocampus in each cerebral hemisphere. If damage to the hippocampus occurs in only one hemisphere, leaving the structure intact in the other hemisphere, the brain can retain near-normal memory functioning. Severe damage to the hippocampi in both hemispheres results in profound difficulties in forming new memories ( anterograde amnesia) and often also affects memories formed before the damage occurred ( retrograde amnesia). Although the retrograde effect normally extends many years back before the brain damage, in some cases older memories remain. This retention of older memories leads to the idea that consolidation over time involves the transfer of memories out of the hippocampus to other parts of the brain. Experiments using intrahippocampal transplantation of hippocampal cells in primates with neurotoxic lesions of the hippocampus have shown that the hippocampus is required for the formation and recall, but not the storage, of memories. It has been shown that a decrease in the volume of various parts of the hippocampus in people leads to specific memory impairments. In particular, efficiency of verbal memory retention is related to the anterior parts of the right and left hippocampus. The right head of the hippocampus is more involved in executive functions and regulation during verbal memory recall. The tail of the left hippocampus tends to be closely related to verbal memory capacity.
Damage to the hippocampus does not affect some types of memory, such as the ability to learn new skills (playing a musical instrument or solving certain types of puzzles, for example). This fact suggests that such abilities depend on different types of memory (procedural memory
Procedural memory is a type of implicit memory (unconscious, long-term memory) which aids the performance of particular types of tasks without conscious awareness of these previous experiences.
Procedural memory guides the processes we perform, ...
) and different brain regions. Furthermore, amnesic patients frequently show "implicit" memory for experiences even in the absence of conscious knowledge. For example, patients asked to guess which of two faces they have seen most recently may give the correct answer most of the time in spite of stating that they have never seen either of the faces before. Some researchers distinguish between conscious ''recollection'', which depends on the hippocampus, and ''familiarity'', which depends on portions of the medial temporal lobe.
When rats are exposed to an intense learning event, they may retain a life-long memory of the event even after a single training session. The memory of such an event appears to be first stored in the hippocampus, but this storage is transient. Much of the long-term storage of the memory seems to take place in the anterior cingulate cortex. When such an intense learning event was experimentally applied, more than 5,000 differently methylated DNA regions appeared in the hippocampus neuronal genome of the rats at one hour and at 24 hours after training. These alterations in methylation
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group on a substrate, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replacing a hydrogen atom. These t ...
pattern occurred at many genes that were down-regulated, often due to the formation of new 5-methylcytosine sites in CpG rich regions of the genome. Furthermore, many other genes were upregulated, likely often due to the removal of methyl groups from previously existing 5-methylcytosines (5mCs) in DNA. Demethylation of 5mC can be carried out by several proteins acting in concert, including TET enzymes as well as enzymes of the DNA base excision repair pathway (see Epigenetics in learning and memory).
Role in spatial memory and navigation
 Studies on freely moving rats and mice have shown many hippocampal neurons to act as
Studies on freely moving rats and mice have shown many hippocampal neurons to act as place cell
A place cell is a kind of pyramidal neuron in the hippocampus that becomes active when an animal enters a particular place in its environment, which is known as the place field. Place cells are thought to act collectively as a cognitive repres ...
s that cluster in place fields, and these fire bursts of action potentials when the animal passes through a particular location. This place-related neural activity in the hippocampus has also been reported in monkeys that were moved around a room whilst in a restraint chair. However, the place cells may have fired in relation to where the monkey was looking rather than to its actual location in the room. Over many years, many studies have been carried out on place-responses in rodents, which have given a large amount of information. Place cell responses are shown by pyramidal cell
Pyramidal cells, or pyramidal neurons, are a type of multipolar neuron found in areas of the brain including the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, and the amygdala. Pyramidal neurons are the primary excitation units of the mammalian prefrontal cor ...
s in the hippocampus and by granule cells in the dentate gyrus. Other cells in smaller proportion are inhibitory interneuron
Interneurons (also called internuncial neurons, relay neurons, association neurons, connector neurons, intermediate neurons or local circuit neurons) are neurons that connect two brain regions, i.e. not direct motor neurons or sensory neurons. I ...
s, and these often show place-related variations in their firing rate that are much weaker. There is little, if any, spatial topography in the representation; in general, cells lying next to each other in the hippocampus have uncorrelated spatial firing patterns. Place cells are typically almost silent when a rat is moving around outside the place field but reach sustained rates as high as 40 Hz when the rat is near the center. Neural activity sampled from 30 to 40 randomly chosen place cells carries enough information to allow a rat's location to be reconstructed with high confidence. The size of place fields varies in a gradient along the length of the hippocampus, with cells at the dorsal end showing the smallest fields, cells near the center showing larger fields, and cells at the ventral tip showing fields that cover the entire environment. In some cases, the firing rate of hippocampal cells depends not only on place but also the direction a rat is moving, the destination toward which it is traveling, or other task-related variables. The firing of place cells is timed in relation to local theta waves
Theta waves generate the theta rhythm, a neural oscillation in the brain that underlies various aspects of cognition and behavior, including learning, memory, and spatial navigation in many animals. It can be recorded using various electrophysio ...
, a process termed phase precession
Phase precession is a neurophysiological process in which the time of firing of action potentials by individual neurons occurs progressively earlier in relation to the phase of the local field potential oscillation with each successive cycle. In ...
.
In humans, cells with location-specific firing patterns have been reported during a study of patients with drug-resistant epilepsy
Drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE), also known as refractory epilepsy or pharmacoresistant epilepsy, is diagnosed when there failure of adequate trials of two tolerated and appropriately chosen and used antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) (whether as monotherapi ...
. They were undergoing an invasive procedure to localize the source of their seizures, with a view to surgical resection. The patients had diagnostic electrodes implanted in their hippocampus and then used a computer to move around in a virtual reality town. Ekstrom et al., 2003 Similar brain imaging studies in navigation have shown the hippocampus to be active. A study was carried out on taxi drivers. London's black cab drivers need to learn the locations of a large number of places and the fastest routes between them in order to pass a strict test known as The Knowledge
Taxicabs are regulated throughout the United Kingdom, but the regulation of taxicabs in London is especially rigorous with regard to mechanical integrity and driver knowledge. An official report observed that: "Little however is known about ...
in order to gain a license to operate. A study showed that the posterior part of the hippocampus is larger in these drivers than in the general public, and that a positive correlation exists between the length of time served as a driver and the increase in the volume of this part. It was also found the total volume of the hippocampus was unchanged, as the increase seen in the posterior part was made at the expense of the anterior part, which showed a relative decrease in size. There have been no reported adverse effects from this disparity in hippocampal proportions. Maguire et al., 2000 Another study showed opposite findings in blind individuals. The anterior part of the right hippocampus was larger and the posterior part was smaller, compared with sighted individuals.
There are several ''navigational cells'' in the brain that are either in the hippocampus itself or are strongly connected to it, such as the speed cells
Speed cells are neurons whose firing rates depend on an animal's speed through its environment. Together with place cells, grid cells, boundary cells, and head direction cells, they form a part of a larger set of neurons that are involved in cogni ...
present in the medial entorhinal cortex. Together these cells form a network that serves as spatial memory. The first of such cells discovered in the 1970s were the place cells, which led to the idea of the hippocampus acting to give a neural representation of the environment in a cognitive map. When the hippocampus is dysfunctional, orientation is affected; people may have difficulty in remembering how they arrived at a location and how to proceed further. Getting lost is a common symptom of amnesia. Studies with animals have shown that an intact hippocampus is required for initial learning and long-term retention of some spatial memory
In cognitive psychology and neuroscience, spatial memory is a form of memory responsible for the recording and recovery of information needed to plan a course to a location and to recall the location of an object or the occurrence of an event. Sp ...
tasks, in particular ones that require finding the way to a hidden goal. Other cells have been discovered since the finding of the place cells in the rodent brain that are either in the hippocampus or the entorhinal cortex. These have been assigned as head direction cell Head direction (HD) cells are neurons found in a number of brain regions that increase their firing rates above baseline levels only when the animal's head points in a specific direction. They have been reported in rats, monkeys, mice, chinchillas a ...
s, grid cell
A grid cell is a type of neuron within the entorhinal cortex that fires at regular intervals as an animal navigates an open area, allowing it to understand its position in space by storing and integrating information about location, distance, and ...
s and boundary cell Boundary cells (also known as border cells or boundary vector cells) are neurons found in the hippocampal formation that respond to the presence of an environmental boundary at a particular distance and direction from an animal. The existence of cel ...
s. Speed cells are thought to provide input to the hippocampal grid cells.
Role in approach-avoidance conflict processing
Approach-avoidance conflict Approach-avoidance conflicts as elements of stress (biology), stress were first introduced by psychologist Kurt Lewin, one of the founders of modern social psychology.
Overview
Approach-avoidance conflicts occur when there is one goal or event that ...
happens when a situation is presented that can either be rewarding
The reward system (the mesocorticolimbic circuit) is a group of neural structures responsible for incentive salience (i.e., "wanting"; desire or craving for a reward and motivation), associative learning (primarily positive reinforcement and class ...
or punishing, and the ensuing decision-making has been associated with anxiety. fMRI findings from studies in approach-avoidance decision-making found evidence for a functional role that is not explained by either long-term memory or spatial cognition. Overall findings showed that the anterior hippocampus is sensitive to conflict, and that it may be part of a larger cortical and subcortical network seen to be important in decision-making in uncertain conditions.
A review makes reference to a number of studies that show the involvement of the hippocampus in conflict tasks. The authors suggest that one challenge is to understand how conflict processing relates to the functions of spatial navigation and memory and how all of these functions need not be mutually exclusive.
Electroencephalography
 The hippocampus shows two major "modes" of activity, each associated with a distinct pattern of
The hippocampus shows two major "modes" of activity, each associated with a distinct pattern of neural population
A neuronal ensemble is a population of nervous system Cell (biology), cells (or Cell culture, cultured neurons) involved in a particular neural computation.
Background
The concept of neuronal ensemble dates back to the work of Charles Sherring ...
activity and waves of electrical activity as measured by an electroencephalogram (EEG). These modes are named after the EEG patterns associated with them: theta and large irregular activity
Large (amplitude) irregular activity (LIA), refers to one of two local field states that have been observed in the hippocampus. The other field state is that of the theta rhythm. The theta state is characterised by a steady slow oscillation of arou ...
(LIA). The main characteristics described below are for the rat, which is the animal most extensively studied.
The theta mode appears during states of active, alert behavior (especially locomotion), and also during REM
Rem or REM may refer to:
Music
* R.E.M., an American rock band
* ''R.E.M.'' (EP), by Green
* "R.E.M." (song), by Ariana Grande
Organizations
* La République En Marche!, a French centrist political party
* Reichserziehungsministerium, in Nazi G ...
(dreaming) sleep. Buzsáki et al., 1990 In the theta mode, the EEG is dominated by large regular waves with a frequency range of 6 to 9 Hz, and the main groups of hippocampal neurons (pyramidal cell
Pyramidal cells, or pyramidal neurons, are a type of multipolar neuron found in areas of the brain including the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, and the amygdala. Pyramidal neurons are the primary excitation units of the mammalian prefrontal cor ...
s and granule cells) show sparse population activity, which means that in any short time interval, the great majority of cells are silent, while the small remaining fraction fire at relatively high rates, up to 50 spikes in one second for the most active of them. An active cell typically stays active for half a second to a few seconds. As the rat behaves, the active cells fall silent and new cells become active, but the overall percentage of active cells remains more or less constant. In many situations, cell activity is determined largely by the spatial location of the animal, but other behavioral variables also clearly influence it.
The LIA mode appears during slow-wave (non-dreaming) sleep, and also during states of waking immobility such as resting or eating. In the LIA mode, the EEG is dominated by sharp waves that are randomly timed large deflections of the EEG signal lasting for 25–50 milliseconds. Sharp waves are frequently generated in sets, with sets containing up to 5 or more individual sharp waves and lasting up to 500 ms. The spiking activity of neurons within the hippocampus is highly correlated with sharp wave activity. Most neurons decrease their firing rate between sharp waves; however, during a sharp wave, there is a dramatic increase in firing rate in up to 10% of the hippocampal population
These two hippocampal activity modes can be seen in primates as well as rats, with the exception that it has been difficult to see robust theta rhythmicity in the primate hippocampus. There are, however, qualitatively similar sharp waves and similar state-dependent changes in neural population activity. Skaggs et al., 2007
Theta rhythm
membrane potential
Membrane potential (also transmembrane potential or membrane voltage) is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell. That is, there is a difference in the energy required for electric charges ...
s and strongly modulate the spiking of hippocampal neurons and synchronise across the hippocampus in a travelling wave pattern. The trisynaptic circuit The trisynaptic circuit, or trisynaptic loop is a relay of Neurotransmission, synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. The circuit was initially described by the neuroanatomist Santiago Ramón y Cajal, Santiago Ramon y Cajal, in the early twentiet ...
is a relay of neurotransmission in the hippocampus that interacts with many brain regions. From rodent studies it has been proposed that the trisynaptic circuit generates the hippocampal theta rhythm.
Theta rhythmicity is very obvious in rabbits and rodents and also clearly present in cats and dogs. Whether theta can be seen in primates is not yet clear. In rats (the animals that have been the most extensively studied), theta is seen mainly in two conditions: first, when an animal is walking or in some other way actively interacting with its surroundings; second, during REM sleep
Rapid eye movement sleep (REM sleep or REMS) is a unique phase of sleep in mammals and birds, characterized by random rapid movement of the eyes, accompanied by low muscle tone throughout the body, and the propensity of the sleeper to dream viv ...
. The function of theta has not yet been convincingly explained although numerous theories have been proposed. Buzsáki, 2006 The most popular hypothesis has been to relate it to learning and memory. An example would be the phase with which theta rhythms, at the time of stimulation of a neuron, shape the effect of that stimulation upon its synapses. What is meant here is that theta rhythms may affect those aspects of learning and memory that are dependent upon synaptic plasticity. It is well established that lesions of the medial septum
The medial septal nucleus (MS) is one of the septal nuclei. Neurons in this nucleus give rise to the bulk of efferents from the septal nuclei. A major projection from the medial septal nucleus terminates in the hippocampal formation.
It plays a ro ...
the central node of the theta systemcause severe disruptions of memory. However, the medial septum is more than just the controller of theta; it is also the main source of cholinergic projections to the hippocampus. It has not been established that septal lesions exert their effects specifically by eliminating the theta rhythm.
Sharp waves
During sleep or during resting, when an animal is not engaged with its surroundings, the hippocampal EEG shows a pattern of irregular slow waves, somewhat larger in amplitude than theta waves. This pattern is occasionally interrupted by large surges called ''sharp waves''. These events are associated with bursts of spike activity lasting 50 to 100 milliseconds in pyramidal cells of CA3 and CA1. They are also associated with short-lived high-frequency EEG oscillations called "ripples", with frequencies in the range 150 to 200 Hz in rats, and together they are known as sharp waves and ripples. Sharp waves are most frequent during sleep when they occur at an average rate of around 1 per second (in rats) but in a very irregular temporal pattern. Sharp waves are less frequent during inactive waking states and are usually smaller. Sharp waves have also been observed in humans and monkeys. In macaques, sharp waves are robust but do not occur as frequently as in rats. One of the most interesting aspects of sharp waves is that they appear to be associated with memory. Wilson and McNaughton 1994, and numerous later studies, reported that when hippocampal place cells have overlapping spatial firing fields (and therefore often fire in near-simultaneity), they tend to show correlated activity during sleep following the behavioral session. This enhancement of correlation, commonly known as ''reactivation'', has been found to occur mainly during sharp waves. It has been proposed that sharp waves are, in fact, reactivations of neural activity patterns that were memorized during behavior, driven by strengthening of synaptic connections within the hippocampus. This idea forms a key component of the "two-stage memory" theory, advocated by Buzsáki and others, which proposes that memories are stored within the hippocampus during behavior and then later transferred to theneocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, sp ...
during sleep. Sharp waves in Hebbian theory are seen as persistently repeated stimulations by presynaptic cells, of postsynaptic cells that are suggested to drive synaptic changes in the cortical targets of hippocampal output pathways. Suppression of sharp waves and ripples in sleep or during immobility can interfere with memories expressed at the level of the behavior, nonetheless, the newly formed CA1 place cell code can re-emerge even after a sleep with abolished sharp waves and ripples, in spatially non-demanding tasks.
Long-term potentiation
Since at least the time of Ramon y Cajal (1852–1934), psychologists have speculated that the brain stores memory by altering the strength of connections between neurons that are simultaneously active. This idea was formalized by Donald Hebb in 1949, but for many years remained unexplained. In 1973,Tim Bliss
Timothy Vivian Pelham Bliss FRS (born 27 July 1940) is a British neuroscientist. He is an adjunct professor at the University of Toronto, and a group leader emeritus at the Francis Crick Institute, London.
In 2016 Professor Tim Bliss shared ...
and Terje Lømo
Terje Lømo (born 3 January 1935) is a Norwegian physiologist who specialized in neuroscience.
He was born in Ålesund to dentist Leif Lømo and Ingeborg Rebekka Helseth.
Lømo in 1966, while beginning his PhD, worked in Per Oskar Andersen's la ...
described a phenomenon in the rabbit hippocampus that appeared to meet Hebb's specifications: a change in synaptic responsiveness induced by brief strong activation and lasting for hours or days or longer. This phenomenon was soon referred to as long-term potentiation (LTP). As a candidate mechanism for long-term memory, LTP has since been studied intensively, and a great deal has been learned about it. However, the complexity and variety of the intracellular signalling cascades that can trigger LTP is acknowledged as preventing a more complete understanding. Malenka & Bear, 2004
The hippocampus is a particularly favorable site for studying LTP because of its densely packed and sharply defined layers of neurons, but similar types of activity-dependent synaptic change have also been observed in many other brain areas. The best-studied form of LTP has been seen in CA1 of the hippocampus and occurs at synapses that terminate on dendritic spines and use the neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neuro ...
glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can syn ...
. The synaptic changes depend on a special type of glutamate receptor, the ''N''-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, a cell surface receptor which has the special property of allowing calcium to enter the postsynaptic spine only when presynaptic activation and postsynaptic depolarization occur at the same time. Nakazawa et al., 2004 Drugs that interfere with NMDA receptors block LTP and have major effects on some types of memory, especially spatial memory. Genetically modified mice that are modified
Modified may refer to:
* ''Modified'' (album), the second full-length album by Save Ferris
* Modified racing, or "Modifieds", an American automobile racing genre
See also
* Modification (disambiguation)
* Modifier (disambiguation)
Modifier may ...
to disable the LTP mechanism, also generally show severe memory deficits.
Disorders
Aging
Age-related conditions such asAlzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term me ...
and other forms of dementia (for which hippocampal disruption is one of the earliest signs) have a severe impact on many types of cognition
Cognition refers to "the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, ...
including memory. Even normal aging is associated with a gradual decline in some types of memory, including episodic memory and working memory (or short-term memory
Short-term memory (or "primary" or "active memory") is the capacity for holding a small amount of information in an active, readily available state for a short interval. For example, short-term memory holds a phone number that has just been recit ...
). Because the hippocampus is thought to play a central role in memory, there has been considerable interest in the possibility that age-related declines could be caused by hippocampal deterioration. Prull et al., 2000, p. 105 Some early studies reported substantial loss of neurons in the hippocampus of elderly people
Old age refers to ages nearing or surpassing the life expectancy of human beings, and is thus the end of the human life cycle. Terms and euphemisms for people at this age include old people, the elderly (worldwide usage), OAPs (British usage ...
, but later studies using more precise techniques found only minimal differences. Similarly, some MRI studies have reported shrinkage of the hippocampus in elderly people, but other studies have failed to reproduce this finding. There is, however, a reliable relationship between the size of the hippocampus and memory performance; so that where there is age-related shrinkage, memory performance will be impaired. Prull et al., 2000, p. 107 There are also reports that memory tasks tend to produce less hippocampal activation in the elderly than in the young. Furthermore, a randomized control trial published in 2011 found that aerobic exercise could increase the size of the hippocampus in adults aged 55 to 80 and also improve spatial memory. Erickson et al., 2011
Stress
The hippocampus contains high levels of glucocorticoid receptors, which make it more vulnerable to long-term stress than most other brain areas. There is evidence that humans having experienced severe, long-lasting traumatic stress show atrophy of the hippocampus more than of other parts of the brain. These effects show up in post-traumatic stress disorder, and they may contribute to the hippocampal atrophy reported in schizophrenia and severe depression. Anterior hippocampal volume in children is positively correlated with parental family income and this correlation is thought to be mediated by income related stress. A recent study has also revealed atrophy as a result of depression, but this can be stopped with anti-depressants even if they are not effective in relieving other symptoms. Chronic stress resulting in elevated levels of glucocorticoids, notably ofcortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone, in the glucocorticoid class of hormones. When used as a medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
It is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland ...
, is seen to be a cause of neuronal atrophy in the hippocampus. This atrophy results in a smaller hippocampal volume which is also seen in Cushing's syndrome. The higher levels of cortisol in Cushing's syndrome is usually the result of medications taken for other conditions. Neuronal loss also occurs as a result of impaired neurogenesis. Another factor that contributes to a smaller hippocampal volume is that of dendritic retraction where dendrites are shortened in length and reduced in number, in response to increased glucocorticoids. This dendritic retraction is reversible. After treatment with medication to reduce cortisol in Cushing's syndrome, the hippocampal volume is seen to be restored by as much as 10%. This change is seen to be due to the reforming of the dendrites. This dendritic restoration can also happen when stress is removed. There is, however, evidence derived mainly from studies using rats that stress occurring shortly after birth can affect hippocampal function in ways that persist throughout life.
Sex-specific responses to stress have also been demonstrated in the rat to have an effect on the hippocampus. Chronic stress in the male rat showed dendritic retraction and cell loss in the CA3 region but this was not shown in the female. This was thought to be due to neuroprotective ovarian hormones. In rats, DNA damage increases in the hippocampus under conditions of stress.
Epilepsy

 The hippocampus is one of the few brain regions where new neurons are generated. This process of
The hippocampus is one of the few brain regions where new neurons are generated. This process of neurogenesis
Neurogenesis is the process by which nervous system cells, the neurons, are produced by neural stem cells (NSCs). It occurs in all species of animals except the porifera (sponges) and placozoans. Types of NSCs include neuroepithelial cells (NECs) ...
is confined to the dentate gyrus. Kuruba et al., 2009 The production of new neurons can be positively affected by exercise or negatively affected by epileptic seizures.
Seizures in temporal lobe epilepsy can affect the normal development of new neurons and can cause tissue damage. Hippocampal sclerosis including Ammon's horn sclerosis
Hippocampal sclerosis (HS) or mesial temporal sclerosis (MTS) is a neuropathological condition with severe neuronal cell loss and gliosis in the hippocampus, specifically in the CA-1 (Cornu Ammonis area 1) and subiculum of the hippocampus. It w ...
that is specific to the mesial temporal lobe, is the most common type of such tissue damage. It is not yet clear, however, whether the epilepsy is usually caused by hippocampal abnormalities or whether the hippocampus is damaged by cumulative effects of seizures. However, in experimental settings where repetitive seizures are artificially induced in animals, hippocampal damage is a frequent result. This may be a consequence of the concentration of excitable glutamate receptors in the hippocampus. Hyperexcitability can lead to cytotoxicity
Cytotoxicity is the quality of being toxic to cells. Examples of toxic agents are an immune cell or some types of venom, e.g. from the puff adder (''Bitis arietans'') or brown recluse spider (''Loxosceles reclusa'').
Cell physiology
Treating cells ...
and cell death. It may also have something to do with the hippocampus being a site where new neurons continue to be created throughout life, and to abnormalities in this process.
Schizophrenia
The causes of schizophrenia are not well understood, but numerous abnormalities of brain structure have been reported. The most thoroughly investigated alterations involve the cerebral cortex, but effects on the hippocampus have also been described. Many reports have found reductions in the size of the hippocampus in people with schizophrenia. Harrison, 2004 The left hippocampus seems to be affected more than the right. The changes noted have largely been accepted to be the result of abnormal development. It is unclear whether hippocampal alterations play any role in causing the psychotic symptoms that are the most important feature of schizophrenia. It has been suggested that on the basis of experimental work using animals, hippocampal dysfunction might produce an alteration of dopamine release in the basal ganglia, thereby indirectly affecting the integration of information in the prefrontal cortex. It has also been suggested that hippocampal dysfunction might account for the disturbances in long-term memory frequently observed. MRI studies have found a smaller brain volume and larger ventricles in people with schizophreniahowever researchers do not know if the shrinkage is from the schizophrenia or from the medication. The hippocampus and thalamus have been shown to be reduced in volume; and the volume of theglobus pallidus
The globus pallidus (GP), also known as paleostriatum or dorsal pallidum, is a subcortical structure of the brain. It consists of two adjacent segments, one external, known in rodents simply as the globus pallidus, and one internal, known in rod ...
is increased. Cortical patterns are altered, and a reduction in the volume and thickness of the cortex particularly in the frontal and temporal lobes has been noted. It has further been proposed that many of the changes seen are present at the start of the disorder which gives weight to the theory that there is abnormal neurodevelopment.
The hippocampus has been seen as central to the pathology of schizophrenia, both in the neural and physiological effects. It has been generally accepted that there is an abnormal synaptic connectivity underlying schizophrenia. Several lines of evidence implicate changes in the synaptic organization and connectivity, in and from the hippocampus Many studies have found dysfunction in the synaptic circuitry within the hippocampus and its activity on the prefrontal cortex. The glutamatergic pathways have been seen to be largely affected. The subfield CA1 is seen to be the least involved of the other subfields, and CA4 and the subiculum have been reported elsewhere as being the most implicated areas. The review concluded that the pathology could be due to genetics, faulty neurodevelopment or abnormal neural plasticity. It was further concluded that schizophrenia is not due to any known neurodegenerative disorder. Oxidative DNA damage
DNA oxidation is the process of oxidative damage of deoxyribonucleic acid. As described in detail by Burrows et al., 8-oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-oxo-dG) is the most common oxidative lesion observed in duplex DNA because guanine has a lower one-e ...
is substantially increased in the hippocampus of elderly patients with chronic schizophrenia.
Transient global amnesia
Transient global amnesia is a dramatic, sudden, temporary, near-total loss of short-term memory. Various causes have been hypothesized including ischemia, epilepsy, migraine and disturbance of cerebral venous blood flow, leading toischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems wi ...
of structures such as the hippocampus that are involved in memory.
There has been no scientific proof of any cause. However, diffusion weighted MRI studies taken from 12 to 24 hours following an episode has shown there to be small dot-like lesions in the hippocampus. These findings have suggested a possible implication of CA1 neurons made vulnerable by metabolic stress.
PTSD
Some studies shows correlation of reduced hippocampus volume and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). A study of Vietnam War combat veterans with PTSD showed a 20% reduction in the volume of their hippocampus compared with veterans having suffered no such symptoms. This finding was not replicated in chronic PTSD patients traumatized at an air show plane crash in 1988 (Ramstein, Germany). It is also the case that non-combat twin brothers of Vietnam veterans with PTSD also had smaller hippocampi than other controls, raising questions about the nature of the correlation. A 2016 study strengthened theory that a smaller hippocampus increases the risk for post-traumatic stress disorder, and a larger hippocampus increases the likelihood of efficacious treatment.Microcephaly
Hippocampus atrophy has been characterized in microcephaly patients and mouse models with WDR62 mutations which recapitulate human point mutations shown a deficiency in hippocampal development and neurogenesis.Other animals

Other mammals
The hippocampus has a generally similar appearance across the range of mammals, frommonotreme
Monotremes () are prototherian mammals of the order Monotremata. They are one of the three groups of living mammals, along with placentals (Eutheria), and marsupials (Metatheria). Monotremes are typified by structural differences in their brain ...
s such as the echidna to primates such as humans. The hippocampal-size-to-body-size ratio broadly increases, being about twice as large for primates as for the echidna. It does not, however, increase at anywhere close to the rate of the neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, sp ...
-to-body-size ratio. Therefore, the hippocampus takes up a much larger fraction of the cortical mantle in rodents than in primates. In adult humans the volume of the hippocampus on each side of the brain is about 3.0 to 3.5 cm3 as compared to 320 to 420 cm3 for the volume of the neocortex.
There is also a general relationship between the size of the hippocampus and spatial memory. When comparisons are made between similar species, those that have a greater capacity for spatial memory tend to have larger hippocampal volumes. Jacobs, 2003 This relationship also extends to sex differences; in species where males and females show strong differences in spatial memory ability they also tend to show corresponding differences in hippocampal volume.
Other vertebrates
Non-mammalian species do not have a brain structure that looks like the mammalian hippocampus, but they have one that is consideredhomologous
Homology may refer to:
Sciences
Biology
*Homology (biology), any characteristic of biological organisms that is derived from a common ancestor
*Sequence homology, biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences
* Homologous chrom ...
to it. The hippocampus, as pointed out above, is in essence part of the allocortex. Only mammals have a fully developed cortex, but the structure it evolved from, called the pallium, is present in all vertebrates, even the most primitive ones such as the lamprey or hagfish. The pallium is usually divided into three zones: medial, lateral and dorsal. The medial pallium forms the precursor of the hippocampus. It does not resemble the hippocampus visually because the layers are not warped into an S shape or enfolded by the dentate gyrus, but the homology is indicated by strong chemical and functional affinities. There is now evidence that these hippocampal-like structures are involved in spatial cognition in birds, reptiles, and fish.
Birds
In birds, the correspondence is sufficiently well established that most anatomists refer to the medial pallial zone as the "avian hippocampus". Numerous species of birds have strong spatial skills, in particular those that cache food. There is evidence that food-caching birds have a larger hippocampus than other types of birds and that damage to the hippocampus causes impairments in spatial memory.Fish
The story for fish is more complex. In teleost fish (which make up the great majority of existing species), the forebrain is distorted in comparison to other types of vertebrates: most neuroanatomists believe that the teleost forebrain is in essence everted, like a sock turned inside-out, so that structures that lie in the interior, next to the ventricles, for most vertebrates, are found on the outside in teleost fish, and vice versa. One of the consequences of this is that the medial pallium ("hippocampal" zone) of a typical vertebrate is thought to correspond to the lateral pallium of a typical fish. Several types of fish (particularly goldfish) have been shown experimentally to have strong spatial memory abilities, even forming "cognitive maps" of the areas they inhabit. There is evidence that damage to the lateral pallium impairs spatial memory. It is not yet known whether the medial pallium plays a similar role in even more primitive vertebrates, such as sharks and rays, or even lampreys and hagfish.Insects and molluscs
Some types of insects, and molluscs such as the octopus, also have strong spatial learning and navigation abilities, but these appear to work differently from the mammalian spatial system, so there is as yet no good reason to think that they have a common evolutionary origin; nor is there sufficient similarity in brain structure to enable anything resembling a "hippocampus" to be identified in these species. Some have proposed, however, that the insect's mushroom bodies may have a function similar to that of the hippocampus. Mizunami et al., 1998Additional images
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
''Hippocampus''
(Wiley) * *
External links
*Hippocampus – Cell Centered Database
Temporal-lobe.com An interactive diagram of the rat parahippocampal-hippocampal region
Search Hippocampus on BrainNavigator
via BrainNavigator {{Authority control Limbic system